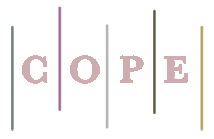In-vitro extraction and separation of copper ions from human blood samples based on amoxicillin/clavulanic acid by ultrasound assisted-dispersive centrifuge liquid-liquid micro extraction
Volume 3, Issue 01, Pages 55-62, Mar 2020 *** Field: Pharmaceutical Analysis
Abstract
The low concentration of copper (Cu2+) can be effected on the central nervous system (CNS) and caused to multiple sclerosis (MS). Although many antibiotics can treat the bacterial infections but some of antibiotics decrease essential metal concentrations in human body and must be controlled by determining. In this study, in-vitro extraction of copper (Cu2+) with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (AMOXC) has been studied due to interacting with metals. By procedure, Cu2+ ions were separated from blood samples by ultrasound assisted-dispersive centrifuge liquid-liquid micro extraction (USA-DC-LLME). The mixture of AMOXC (0.01 g), ionic liquid ([BMIM][PF6]) and acetone injected to 10 ml of serum blood sample at human pH=7.2. After extraction, the concentration of Cu2+ ions was determined by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (F-AAS). The LOD, enrichment factor (EF), linear range (LR) and working range (WR) were obtained 6 μg L-1, 9.92, 0.018-0.5 mg L-1 and 0.02-2.58 mg L-1, respectively (RSD<1.1%).
References
G.F. Nordberg, B.A. Fowler, M. Nordberg, Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, (Fourth ed.), Academic Press, 2014.
H.P. Roeser, G.R. Lee, S. Nacht, G.E. Cartwright, The role of caeruloplasmin in iron metabolism, J. Clin. Invest., 49 (1970) 2408-2417.
S. Catalani, M. Paganelli, M. Enrica Gilberti, L. Rozzini, F. Lanfranchi, A. Padovani, P. Apostol, Free copper in serum: An analytical challenge and its possible applications, J. Trace Elem.Med. Biol., 45 (2018)176-180.
R. Squitti, Copper in Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis of serum plasma, and cerebrospinal fluid studies, J. Alzheimers Dis., 24 (2011) 175-185.
B.S. Choi, W. Zheng, Copper transport to the brain by the blood-brain barrier and blood-CSF barrier, Brain Res., 1248 (2009) 14-21.
Y.U. Fengxiang, P. Gong, Z. Hu, Y. Qiu, Y. Cui, X. Gao, H. Chen, J. Li, Cu(II) enhances the effect of Alzheimer’s amyloid-β peptide on microglial activation, J. Neuroinflamm., 12 (2015)122.
S. Bolognin, L. Messori, D. Drago, C. Gabbiani, L. Cendron, P. Zatta, Aluminum, copper, iron and zinc differentially alter amyloid-Aβ1-42 aggregation and toxicity, Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 43 (2011) 877–85.
X.Y. Choo, L. Alukaidey, A.R. White, A. Grubman, Neuroinflammation and copper in Alzheimer’s disease, Int. J. Alzheimers Dis., 2013 (2013) 145345.
LM Gaetke, copper: toxicological relevance and mechanisms, Arch. Toxicol., 88 (2014) 1929-1938
S. Radi, S. Tighadouini, M. Bacquet, S. Degoutin, Y. Garcia, New hybrid material based on a silicaimmobilised conjugated β-ketoenol-bipyridine receptor and its excellent Cu (II) adsorption capacity, Anal. Method., 8 (2016) 6923–6931.
S. Tighadouini, S. Radi, M. Bacquet, S. Degoutin, M. Zaghrioui, S. Jodeh, I Warad, Removal efficiency of Pb (II), Zn (II), Cd (II) and Cu (II) from aqueous solution and natural water by ketoenol–pyrazole receptor functionalized silica hybrid adsorbent, Sep. Sci. Technol., 52 (2017) 608–621.
A. Prkić, I. Mitar , J. Giljanović, V. Sokol, P. Bošković, I. Dolanc, T. Vukušić, Comparison of Potentiometric and ETAAS Determination of Copper and Iron in Herbal Samples, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 13 (2018) 9551 – 9560.
S. Catarino, A. S. Curvelo-Garcia, Determination of copper in wine by ETAAS using conventional and fast thermal programs: Validation of analytical method, Atom. Spect. Norwalk Connecticut, 26 (2005) 73-78.
E. A. Al‐Harbi, M. S. El‐Shahawi, Square wave‐anodic stripping voltammetric determination of copper at a bismuth film/glassy carbon electrode using 3‐[(2‐Mercapto‐Vinyl)‐Hydrazono]‐ 1,3‐dihydro‐indol, Electroanal., 30 (2018) 1583-1885.
J. F. Ayala-Cabrera, M. J. Trujillo-Rodríguez, V. Pino, Ó. M. Hernández-Torres, A. M. Afonso, J. Sirieix-Plénet, Ionic liquids versus ionic liquidbased surfactants in dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for determining copper in water by flame atomic absorption spectrometry, Inter. J. Environ. Anal. Chem., 96 (2016) 101–118.
N. Bader, H. Hasan, A. EL-Denali, Determination of Cu, Co, and Pb in selected frozen fish tissues collected from Benghazi markets in Libya, Chem. Methodol., 2 (2018) 56-63
M. Soylak, O. Ercan, Selective separation and preconcentration of copper (II) in environmental samples by the solid phase extraction on multiwalled carbon nanotubes, J. Hazard. Mater., 168 (2009) 1527-1531.
C. Duran, A. Gundogdu, V. N. Bulut, M. Soylak, L. Elci, H. B. Sentürk, M. Tüfekci, Solid-phase extraction of Mn (II), Co (II), Ni (II), Cu (II), Cd (II) and Pb (II) ions from environmental samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS), J. Hazard. Mater., 146 (2007) 347-355.
Y. M. Hao, C. Man, Z. B. Hu, Effective removal of Cu2+ ions from aqueous solution by aminofunctionalized magnetic nanoparticles, J. Hazard. Mater., 184 (2014) 392–399.
Y. T. Zhou, H. L. Nie, C. B. White, Removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solution by chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles modified with αketoglutaric acid, J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 330 (2009) 29–37.
S. Golkhah, H. Zavvar Mousavi, H. Shirkhanloo, A. Khaligh, Removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles, Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 13 (2017) 105-117.
A. Sarı, M. Tuzen, D. Cıtak, M. Soylak, Adsorption characteristics of Cu (II) and Pb (II) onto expanded perlite fromaqueoussolution, J. Hazard. Mater., 148 (2007) 387-394.
S. A. Arain, T. G. Kazi, H. I. Afridi, M. Shahzadi Arain, A. H. Panhwar, N. Khan, J. A. Baig, F. Shah, A new dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction using ionic liquid based microemulsion coupled with cloud point extraction for determination of copper in serum and water samples, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety, 126 (2016) 186–192.
A.T. Bisgin, Surfactant-Assisted Emulsification and Surfactant-Based Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Method for Determination of Cu(II) in Food and Water Samples by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, J. AOAC Inter., 102 (2019) 1516-1522.
Copyright (c) 2020 Analytical Methods in Environmental Chemistry Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
JOURNAL PUBLISHING AGREEMENT
PLEASE PROVIDE US THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION,
Article entitled:
Corresponding author:
To be published in the journal:
Your Status
I am the sole author of the manuscript
- I am an Iranian government employee.
- I am a European government employee
- I am a Asian government
- None of the above
I am one author signing on behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript
- I am an Iranian government employee.
- I am a European government employee
- I am a Asian government
- None of the above
Please tick the above blanks (as appropriate), review the Journal Publishing Agreement, and then sign and date the document in black ink.
Published Journal Article: the author may share a link to the formal publication through the relevant DOI. Additionally theses and dissertations which contain embedded Published Journal Articles as part of the formal submission may be hosted publicly by the awarding institution with a link to the formal publication through the relevant DOI. Any other sharing of Published Journal Articles is by agreement with the publisher only.
Signed: ______________________________________ Name printed: ___________________________________________
Title and Company (if employer representative): _______________________Date: __________________________________